After some analysis, digging information, and putting it all together, we came up with this "Osteoporosis: Understand The Causes, Symptoms, And Treatments For Bone Health" guide to provide you with information about what osteoporosis is and how to prevent it. Keep reading to know more.
FAQ
Osteoporosis is a condition that makes bones weak and brittle, increasing the risk of fractures. It's essential to understand the underlying causes, symptoms, and treatment options to maintain bone health. Here are some frequently asked questions and answers to shed light on this topic:
/osteoporosis-5c40ab9746e0fb0001af2d87.jpg)
Osteoporosis: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment - Source www.verywellhealth.com
Question 1: What are the primary causes of osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis is often associated with aging, as bone mass naturally declines after reaching the peak in adulthood. However, various factors can contribute to its development. These include hormonal imbalances, such as estrogen deficiency in postmenopausal women, certain medications, chronic diseases like diabetes and rheumatoid arthritis, and lifestyle habits such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Question 2: What are the common symptoms of osteoporosis?
In its early stages, osteoporosis may not present any noticeable symptoms. As it progresses, individuals may experience back pain, bone fractures, height loss, stooped posture, and increased risk of fractures from minor falls or activities.
Question 3: How is osteoporosis diagnosed?
Diagnosis of osteoporosis typically involves a combination of physical exams, medical history assessment, and bone density tests. Bone density tests measure the mineral content of bones, providing insights into bone strength and density. These tests help determine if an individual has osteoporosis or is at risk of developing it.
Question 4: What are the treatment options for osteoporosis?
Treatment plans for osteoporosis aim to strengthen bones, prevent further bone loss, and reduce the risk of fractures. These may include lifestyle modifications, such as regular weight-bearing exercises, a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, and quitting smoking. Medications like bisphosphonates, denosumab, and teriparatide may also be prescribed to increase bone density and prevent fractures.
Question 5: How can osteoporosis be prevented?
While osteoporosis may be an age-related condition, several preventive measures can be taken. These include maintaining a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise, consuming an adequate amount of calcium and vitamin D, avoiding excessive alcohol and tobacco use, and consulting with a healthcare professional about bone health and any underlying medical conditions that could contribute to bone loss.
Question 6: Is osteoporosis a serious condition?
Osteoporosis is a serious condition that can lead to painful fractures, reduced mobility, and even disability. It's important to seek early diagnosis and treatment to maintain bone health, prevent fractures, and improve overall quality of life.
Understanding osteoporosis and its implications is crucial for maintaining bone health and preventing fractures. Remember, it's never too late to take preventive measures and seek medical advice if you have concerns about bone loss or osteoporosis.
For further information and support, consider consulting with a healthcare professional or exploring reliable resources from organizations such as the National Osteoporosis Foundation.
Tips
For individuals concerned about bone health, "Osteoporosis: Understand The Causes, Symptoms, And Treatments For Bone Health" provides valuable information and actionable tips to maintain strong and healthy bones:
Tip 1: Ensure Adequate Calcium Intake
Calcium is crucial for building and maintaining bone density. Aim for 1,000-1,200 milligrams of calcium daily through dietary sources like dairy products, leafy green vegetables, or fortified foods. If dietary intake is insufficient, consider calcium supplements as recommended by a healthcare professional.
Tip 2: Engage in Regular Weight-Bearing Exercise
Weight-bearing exercises such as walking, running, or dancing apply stress on bones, stimulating their growth and strengthening. Inactivity, on the other hand, can lead to bone loss. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity weight-bearing exercise weekly.
Tip 3: Optimize Vitamin D Levels
Vitamin D aids in calcium absorption and bone mineralization. Sunlight exposure is a natural source of vitamin D. However, if sunlight exposure is limited or inadequate, consider dietary sources like fatty fish (e.g., salmon, tuna), fortified foods, or supplements as advised by a doctor.
Tip 4: Quit Smoking and Limit Alcohol Consumption
Smoking and excessive alcohol intake negatively impact bone health. Smoking disrupts bone formation, while alcohol can interfere with calcium absorption and increase the risk of falls, leading to fractures.
Tip 5: Maintain a Healthy Weight
Being underweight or overweight can affect bone density. A healthy weight helps reduce the risk of fractures and promotes overall bone health.
Tip 6: Consult a Healthcare Professional
Regular bone density screenings and consultations with a healthcare professional are crucial for monitoring bone health, identifying any underlying issues, and receiving appropriate treatment recommendations.
Tip 7: Consider Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
For postmenopausal women, HRT may help prevent bone loss by replenishing estrogen levels, which decline after menopause and contribute to osteoporosis. However, HRT should be discussed with a healthcare provider to assess individual risks and benefits.
Tip 8: Stay Informed and Seek Additional Resources
Knowledge is power when it comes to bone health. Stay informed about osteoporosis, its causes, symptoms, and treatments. Consider referring to reputable sources such as the National Osteoporosis Foundation or consulting with a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and support.
By following these tips, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain healthy bones throughout their lives, reducing the risk of osteoporosis and its associated complications.
For a comprehensive understanding of osteoporosis and its management, explore the informative article, "Osteoporosis: Understand The Causes, Symptoms, And Treatments For Bone Health"
Osteoporosis: Understand The Causes, Symptoms, And Treatments For Bone Health
Osteoporosis is a disease that weakens bones, making them more susceptible to fractures. It is a major public health concern, affecting millions of people worldwide. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments of osteoporosis is crucial for maintaining bone health and preventing fractures.
- Causes: Age, menopause, certain medications, and lifestyle factors can contribute to osteoporosis.
- Symptoms: Osteoporosis often goes unnoticed in its early stages. As it progresses, it can cause back pain, loss of height, and increased risk of fractures.
- Diagnosis: A bone density test is the primary method for diagnosing osteoporosis. It measures the density of bones to assess their strength.
- Treatments: Medications, dietary changes, and exercise can help slow down bone loss and prevent fractures.
- Prevention: Maintaining a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can help prevent osteoporosis.
- Lifestyle: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular weight-bearing exercises, can help improve bone strength and reduce the risk of osteoporosis.
Understanding these key aspects of osteoporosis is essential for maintaining bone health and preventing fractures. By addressing the causes, managing the symptoms, and implementing preventative measures, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their bone health and ensure their overall well-being.
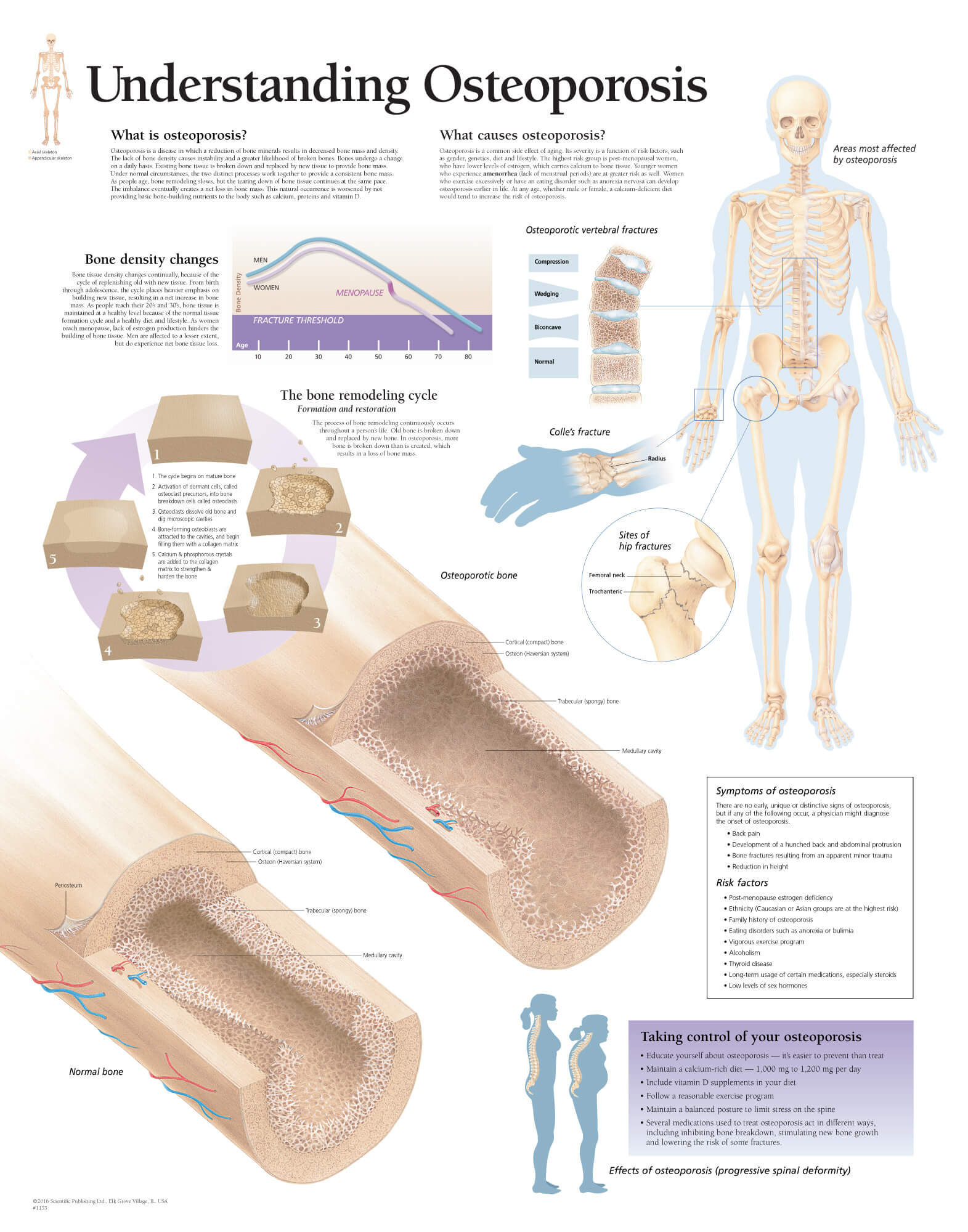
Understanding Osteoporosis | Scientific Publishing - Source www.scientificpublishing.com
Osteoporosis: Understand The Causes, Symptoms, And Treatments For Bone Health
Osteoporosis is a bone disease that occurs when the body loses too much bone, makes too little bone, or both. As a result, bones become weak and may break from a fall or, in serious cases, from sneezing or minor bumps. Osteoporosis is a major public health problem, affecting an estimated 10 million Americans over the age of 50. Women are more likely to develop osteoporosis than men, and the risk increases with age.

Definition & causes of Osteoporosis | PPT - Source www.slideshare.net
There are several risk factors for osteoporosis, including:
- Age: The risk of osteoporosis increases with age.
- Sex: Women are more likely to develop osteoporosis than men.
- Race: White and Asian people are more likely to develop osteoporosis than Black and Hispanic people.
- Family history: People with a family history of osteoporosis are more likely to develop the disease.
- Certain medical conditions: People with certain medical conditions, such as Cushing's syndrome, diabetes, and rheumatoid arthritis, are more likely to develop osteoporosis.
- Certain medications: Some medications, such as steroids and certain cancer drugs, can increase the risk of osteoporosis.
- Lifestyle factors: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and a lack of exercise can increase the risk of osteoporosis.
The symptoms of osteoporosis often do not appear until a bone is broken. However, some people with osteoporosis may experience back pain, a loss of height, or a stooped posture. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to see your doctor for a diagnosis.
There are several treatments available for osteoporosis. These treatments include:
- Medication: There are several medications available to treat osteoporosis, including bisphosphonates, denosumab, and teriparatide.
- Lifestyle changes: Making healthy lifestyle changes, such as eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and quitting smoking, can help to prevent and treat osteoporosis.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair a broken bone or to prevent further fractures.
Osteoporosis is a serious disease, but it can be prevented and treated. If you are at risk for osteoporosis, talk to your doctor about ways to prevent the disease. If you have osteoporosis, talk to your doctor about treatment options.
Conclusion
Osteoporosis is a debilitating disease, but it can be prevented and treated. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments of osteoporosis, you can take steps to protect your bone health and prevent fractures.
If you are at risk for osteoporosis, talk to your doctor about ways to prevent the disease. If you have osteoporosis, talk to your doctor about treatment options. With proper care, you can live a long, healthy life with osteoporosis.