Dow Jones Industrial Average: Market Movements And Analysis is a well-known topic in the financial world. By covering recent market movements and in-depth analysis, we have created a guide for you to understand the significance of Dow Jones Industrial Average: Market Movements And Analysis.
Editor's Notes: Dow Jones Industrial Average: Market Movements And Analysis has been published today to help you stay up-to-date on one of the most widely followed stock market indices. This exclusive article offers insights into its composition, history, and factors driving its movements.
To guide our target audience in making well-informed decisions, our dedicated team has done extensive research and analysis, resulting in this comprehensive Dow Jones Industrial Average: Market Movements And Analysis guide.
| Key Differences | Key Takeaways |
|---|---|
| Understanding the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) | DJIA is a price-weighted index composed of 30 prominent blue-chip stocks. |
| Historical Significance and Evolution | DJIA holds historical significance as the second-oldest stock market index, providing a snapshot of the U.S. economy. |
| Factors Influencing DJIA Movements | Economic indicators, corporate earnings, and global events impact DJIA's movements. |
| Importance for Market Participants | DJIA serves as a benchmark for investors, analysts, and policymakers. |
If you want to understand the impact of macroeconomic factors, global trends, and industry-specific news on the stock market, this Dow Jones Industrial Average: Market Movements And Analysis guide will help you.
FAQ
This section addresses frequently asked questions about the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA), providing clear and informative answers to common inquiries.
Dow Jones Performance Ytd 2024 - Toma Agnella - Source nediqlilias.pages.dev
Question 1: What is the Dow Jones Industrial Average?
The DJIA is a stock market index that measures the performance of 30 large, publicly traded companies in the United States. It is one of the oldest and most widely followed stock indices, often used as a barometer of the overall health of the US equity market.
Question 2: How is the DJIA calculated?
The DJIA is calculated by dividing the sum of the share prices of the 30 component companies by the Dow Divisor. The Dow Divisor is a constantly changing factor that adjusts for stock splits and other corporate actions to ensure the index remains representative.
Question 3: What are the key factors that influence the DJIA?
The DJIA can be influenced by various factors, including economic data, geopolitical events, corporate earnings reports, and investor sentiment. Changes in interest rates, inflation, and consumer spending can also impact the index.
Question 4: Is the DJIA a good indicator of the overall market?
While the DJIA is a widely recognized market indicator, it does not represent the entire US stock market. It focuses on a limited number of large, established companies and may not fully reflect the performance of the broader market.
Question 5: Why has the DJIA performed well recently?
The DJIA's recent performance can be attributed to a combination of factors, including strong corporate earnings, positive economic data, and investor optimism about the future of the US economy.
Question 6: What are some potential risks to the DJIA?
The DJIA, like any stock market index, faces potential risks such as economic downturns, geopolitical instability, and changes in investor sentiment. Slowing economic growth, rising interest rates, or a loss of investor confidence can negatively impact the index.
It is crucial to note that the DJIA is a historical index that does not predict future performance. Investors should seek professional financial advice before making any investment decisions.
Next Article: Examining the Performance of the Dow Jones Industrial Average
Tips
Tracking the Dow Jones Industrial Average: Market Movements And Analysis can provide valuable insights for investors. Here are some tips to effectively analyze market movements:

Dow Jones Shakes Up: Nvidia Replaces Intel | Plus500 - Source www.plus500.com
Tip 1: Understand the Index Composition
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) comprises 30 large-cap U.S. companies from various industries. Understanding the sector and company weights can help you gauge the overall market direction.
Tip 2: Monitor Economic Data
Economic indicators such as GDP, employment figures, and inflation rates can impact DJIA performance. Keeping an eye on these data releases can provide context for market movements.
Tip 3: Analyze Industry Trends
Industry-specific factors, such as technological advancements or regulatory changes, can influence the performance of companies in the DJIA. Monitor industry news and reports to identify potential drivers and headwinds.
Tip 4: Consider Technical Analysis
Technical analysis involves studying price charts to identify patterns and trends. It can help you identify potential support and resistance levels, providing insights into potential market reversals.
Tip 5: Seek Professional Guidance
If you are new to market analysis, it is advisable to seek professional guidance from financial advisors or analysts. They can provide personalized insights based on your investment objectives.
By implementing these tips, investors can enhance their understanding of the DJIA and make more informed investment decisions.
These tips can help you analyze the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) effectively, providing you with valuable insights into market movements and investment opportunities.
Dow Jones Industrial Average: Market Movements And Analysis
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) is a widely followed stock market index that tracks the performance of 30 large, publicly traded companies in the United States. It is considered a benchmark for the overall health of the U.S. stock market and is closely watched by investors, analysts, and the media. Key aspects of the DJIA's market movements and analysis include:
- Composition: The DJIA is composed of 30 companies selected by the editors of The Wall Street Journal based on factors such as market capitalization, industry representation, and historical significance.
- Price-Weighted: Unlike other indices like the S&P 500, the DJIA is price-weighted, meaning the stock price of each component company has a direct impact on the index's value.
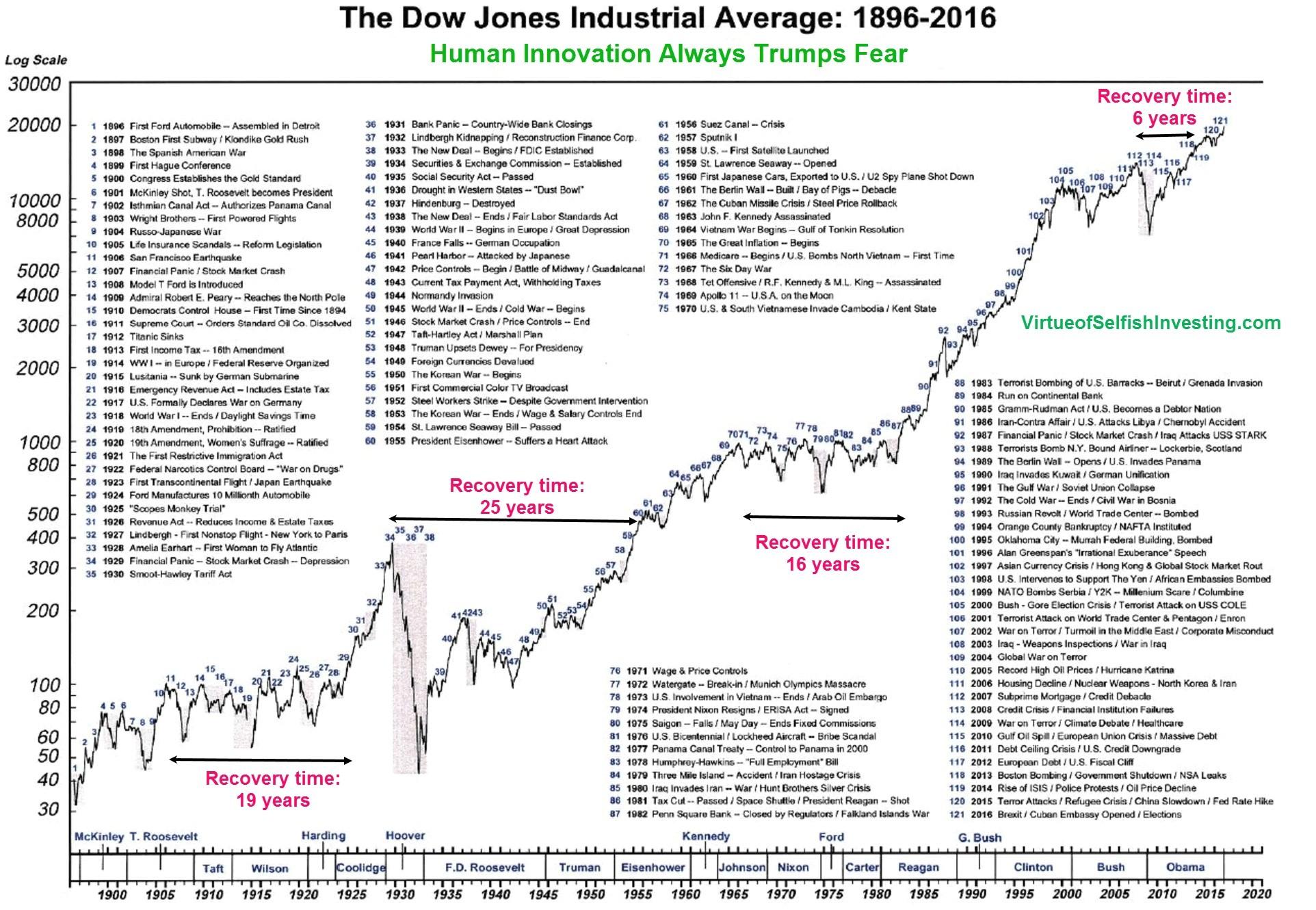
- Historical Significance: The DJIA is one of the oldest stock market indices in the world, dating back to 1896. It has witnessed numerous market events, economic cycles, and historical milestones.
- Market Sentiment: The DJIA is often viewed as a barometer of market sentiment. Strong gains or losses in the index can indicate investor optimism or pessimism.
- Volatility: The DJIA can be volatile, experiencing significant fluctuations in value over short periods of time. Factors such as economic news, corporate earnings, and geopolitical events can contribute to its volatility.
- Economic Indicator: The DJIA is sometimes used as an indicator of the overall health of the U.S. economy. A rising DJIA may suggest economic growth, while a declining DJIA may indicate economic weakness.
In conclusion, the Dow Jones Industrial Average is a key market index that provides insights into the health of the U.S. stock market. Its composition, price-weighting, historical significance, market sentiment, volatility, and correlation with the economy make it an important tool for investors and analysts seeking to understand market movements and trends.

Dow Jones December Outlook: A Crash or Santa Rally? - Source marketrealist.com

Unveiling Market Trends: Dow Jones Industrial Average Takes a Dip After - Source findggle.com
Dow Jones Industrial Average: Market Movements And Analysis
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) is a stock market index that tracks the stock performance of 30 large, publicly-traded companies in the United States. It is one of the most widely used and well-known stock market indices in the world, and its movements are closely watched by investors and financial analysts alike.
Dow Jones - Live Chart, Technical Analysis & Why Trade DJI - Source www.atfx.com
The DJIA is calculated by taking the sum of the stock prices of the 30 companies included in the index and dividing by a divisor that is adjusted to keep the index value relatively stable over time. The index is updated in real-time throughout the trading day, and its movements are widely reported in the financial press.
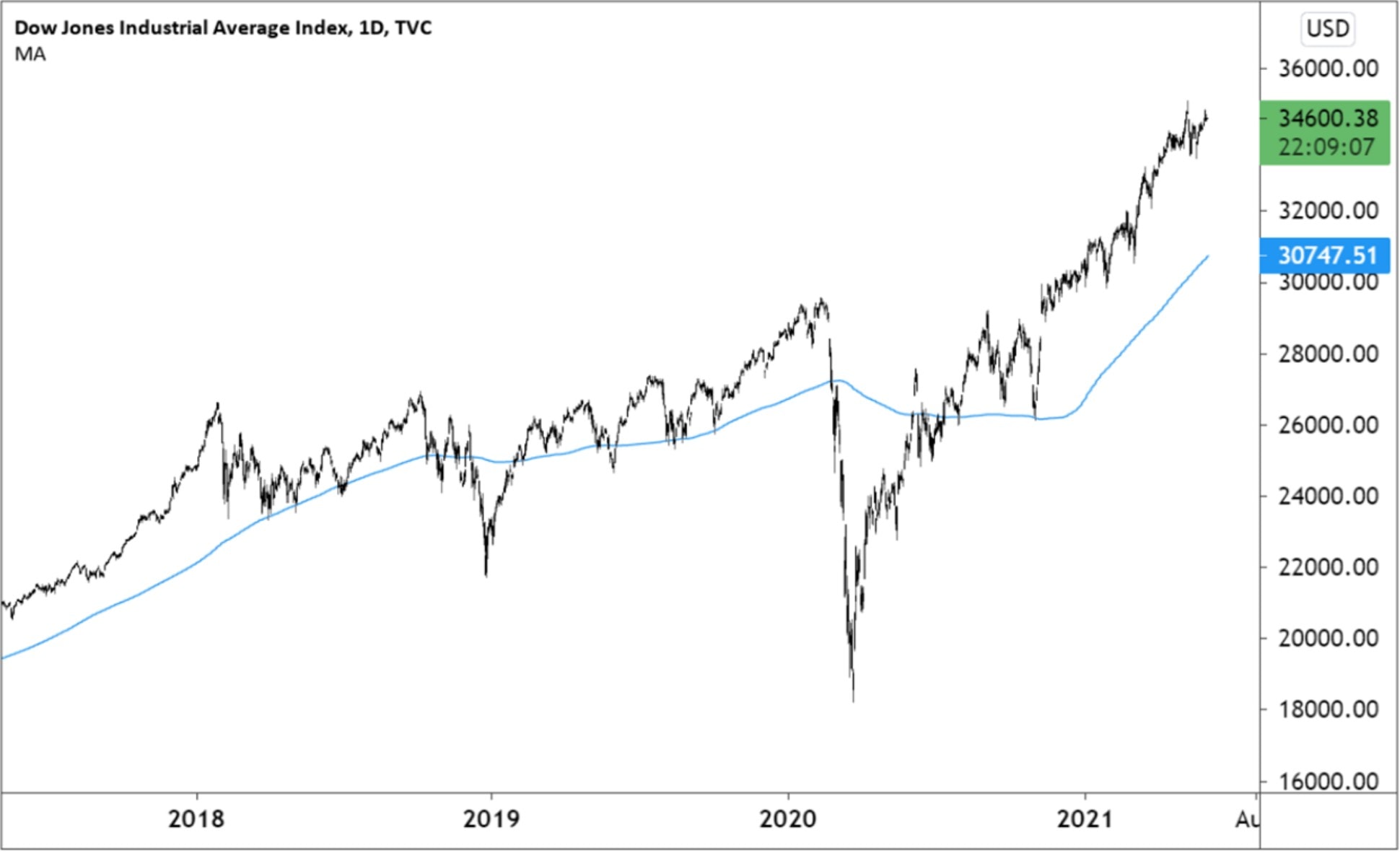
The DJIA is a barometer of the overall health of the U.S. stock market, and its movements can be used to gauge investor sentiment and the overall direction of the market. A rising DJIA typically indicates that investors are optimistic about the future of the economy, while a falling DJIA can indicate that investors are pessimistic.
The DJIA is also used as a benchmark for other stock market indices, and its movements can have a ripple effect on other markets around the world. For example, a sharp decline in the DJIA can lead to selloffs in other stock markets, while a strong rally in the DJIA can boost investor confidence and lead to rallies in other markets.
The DJIA is a valuable tool for investors and financial analysts, and its movements can provide important insights into the overall health of the U.S. stock market and the global economy.
Conclusion
The Dow Jones Industrial Average is a widely used and well-known stock market index that tracks the stock performance of 30 large, publicly-traded companies in the United States. Its movements are closely watched by investors and financial analysts alike, and it is considered a barometer of the overall health of the U.S. stock market.
The DJIA is calculated by taking the sum of the stock prices of the 30 companies included in the index and dividing by a divisor that is adjusted to keep the index value relatively stable over time. The index is updated in real-time throughout the trading day, and its movements are widely reported in the financial press.
The DJIA is a valuable tool for investors and financial analysts, and its movements can provide important insights into the overall health of the U.S. stock market and the global economy.